Enterprise Resource Planning Definition
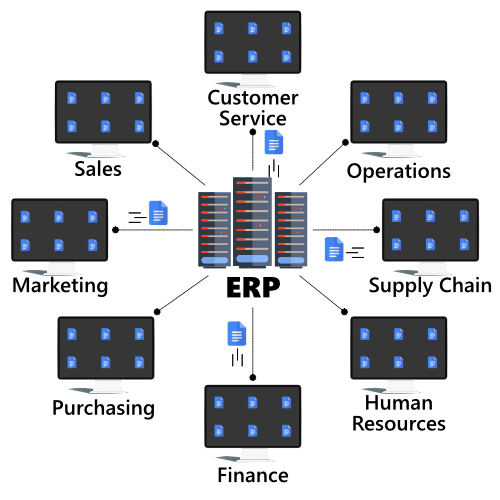
Enterprise Resource Planning or ERP is often not a standalone system but features many different ERP modules to manage different parts of your business. However, at its core, ERP applications are developed to streamline and automate business processes, provide businesses with important insights, give internal control over data, and centralizing all the data sources into one central database.
The main central database collects input from departments such as finance, accounting, purchasing, manufacturing, supply chain, sales, marketing, human resources, and others. Also if needed it can draw data from third-party tools as well to create 360-degree visibility of the business and not having data in silos.
ERP systems are designed to be the central database of all your data. This helps ensure that the information across the business and departments is normalized and can be accessed with permission. Of course, depending on the level of permission, role, and other aspects, the user can access a certain amount of data.
Let’s give an example.
A company that creates sneakers and gets its raw material such as rubber, textile, and plastic from multiple suppliers. To effectively manage the business processes, inventory, and production, a company could use an ERP system to track the stock of raw materials and purchasing of these materials to ensure the entire process of purchasing, delivering, and storing is according to the SOP of the business and clean data are collected to create reporting and analytics. Then the company can use the ERP system to gain important information about the business. (Check out Best Manufacturing ERP Systems in Malaysia)
For example, different types of “shoelaces” can be easily identified by part name, size, material, source, lot number, supplier part number, serial number, cost, and specification, along with more information.
And because visibility into data is essential for business, ERP makes it easy to collect, organize, analyze and distribute any given information to every individual and system that requires such information to effectively carry on their role and responsibilities.
Thus, the person in charge can make an informed decision, whether they are short of stock, having too much stock along with identifying any trends that business could capitalize on. Not only that, but ERP also ensures all your data fields are standardized and everybody uses the same terms for each individual item to avoid any mistakes.
Especially when tracking the cost of an individual team. If the company uses 10 different material textile to produce their shoes, then it is essential to track correctly every single material, its cost, quantity, and how much it has been used. This enables a company to identify whether the price of the material is too high and can be negotiated and also predict how much they need to stock the right amount without running out of stock or over-ordering.
The key ERP principle is to centralize data collection across organizations and help companies to avoid using separate and disconnected systems that do not communicate with each other. Which results in endless copy and pasting of data from one system to another with a high risk of making mistakes. ERP System is meant to clear all that, organize and automate your data, and get the right and clean data from CEO to office clerk.
Of course, many ERP systems provide high enterprise-level security so everyone can access confidently their company data and work with them in real-time. This brings the company clear, up-to-date, and complete data visibility.
Why is ERP System Important?
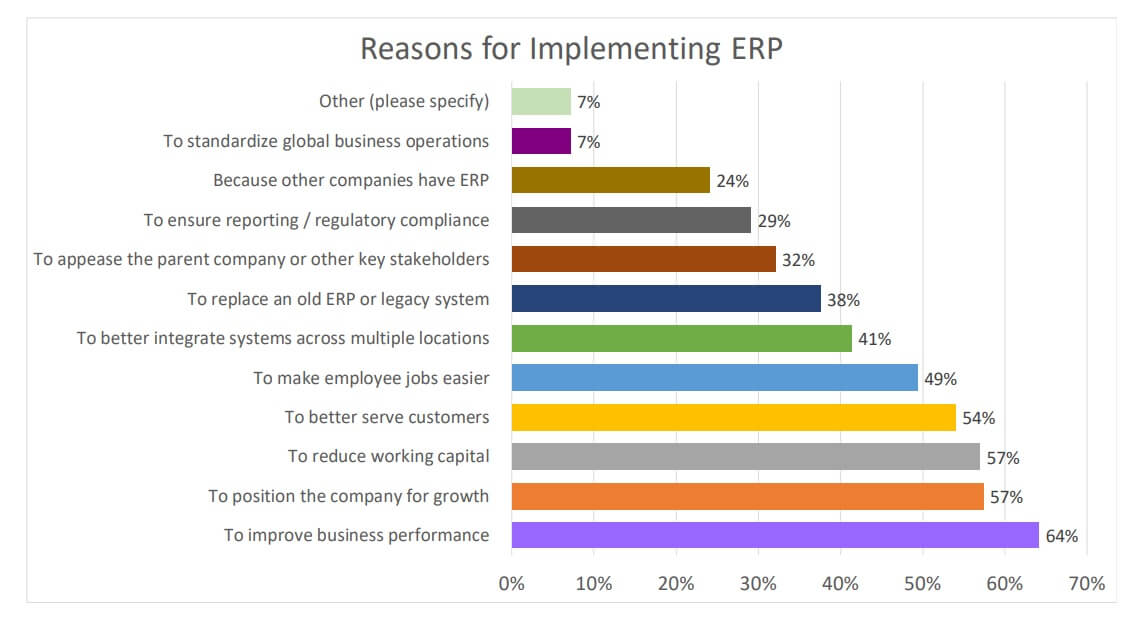
If you are considering implementing an ERP system, upgrading or you are not sure if you actually need an ERP system for your business, then it’s worthwhile to look at some of the reasons why other companies in your industry have invested in the ERP system.