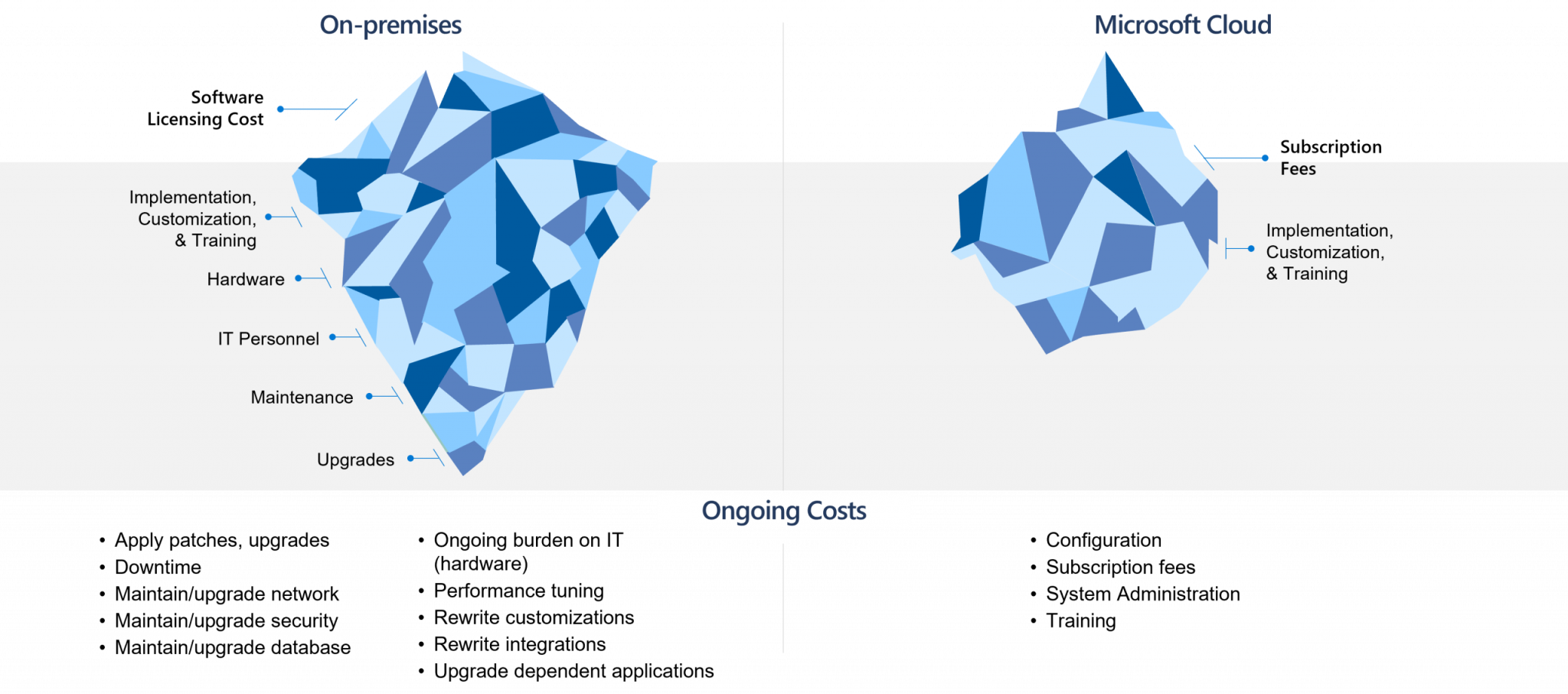
- On-premise ERP: Involves installing and hosting the ERP system on the company’s own servers and infrastructure. This option usually requires a larger upfront investment in hardware, such as servers, storage, and networking equipment, as well as ongoing maintenance and support costs.
- Cloud-based ERP: Hosted and managed by a third-party provider, reducing the need for businesses to invest in their own hardware and infrastructure. Instead, they pay a subscription fee to the provider, which covers the cost of hosting, maintenance, and support. This option typically has lower upfront costs and can be more easily scaled as the business grows.
Learn more on How ERP system can be deployed.
Hardware and Networking Requirements:
- Server capacity: For on-premise ERP implementations, businesses need to invest in servers that can handle the processing and storage requirements of the system. The cost of servers depends on factors such as processing power, storage capacity, and redundancy features.
- Networking equipment: On-premise ERP systems require networking equipment like switches, routers, and firewalls to connect the servers with the users and ensure data security. The costs of this equipment can vary depending on the size and complexity of the network.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Both on-premise and cloud-based ERP systems require robust backup and disaster recovery solutions to ensure business continuity in case of data loss or system failure. These solutions can add to the overall cost of hardware and infrastructure. However, cloud-based often have this included in the pricing.
- Power and cooling: On-premise ERP systems often require additional power and cooling resources to support the servers, which can contribute to the ongoing operational expenses of the system.
Most of the ERP software such as Dynamics 365 provides on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid version to cater your business needs.
Customization and integration
Every business has unique processes and requirements, which may necessitate customizing and integrating the chosen ERP system with other existing business systems to maximize the ERP benefits.
These factors can significantly affect the overall cost of ERP implementation in fact, in most cases it makes up the significant part of the one-time cost.
In this section, we will discuss the implications of customization and integration on ERP implementation costs.
Customizing ERP to Meet Unique Business Needs:
- Tailoring the system: Businesses often need to modify or configure the standard ERP system to meet their specific requirements, such as industry-specific functionalities or custom workflows. The extent of customization required will directly impact the implementation costs.
- Development resources: Customizing an ERP system may require hiring external consultants or allocating internal resources to develop the necessary modifications, which can add to the overall project cost.
- Testing and validation: Customized ERP solutions require thorough testing and validation to ensure that they function correctly and meet the desired business objectives. This process can be time-consuming and costly.
Integrating ERP with Other Business Systems:
- Data integration: Businesses often need to integrate their ERP system with other existing systems, such as CRM, HR, or finance software. This process involves data mapping and synchronization, which can be complex and costly, depending on the number of systems involved and their compatibility.
- Middleware and APIs: Integrating ERP systems with other applications often requires middleware or APIs to facilitate data exchange between the systems. The cost of these tools and the resources needed to develop and maintain the integrations can add to the overall implementation expenses.
- Ongoing maintenance: Integrations between the ERP system and other applications may require regular maintenance to ensure they continue to function correctly, especially when updates or changes are made to any of the systems involved. This maintenance can result in additional ongoing costs.
Training and support
Implementing an ERP system often involves a significant learning curve for employees who will be using the system. Additionally, ongoing support and maintenance are crucial to ensure the system functions smoothly and adapts to evolving business needs.
Both training and support can have a considerable impact on the overall cost of ERP implementation. In this section, we will discuss these factors in detail.
Training Employees to Use the ERP System:
- Training methods: Different ERP vendors offer various training methods, such as instructor-led sessions, online courses, or self-paced learning materials. The chosen method and the extent of training required can affect the training costs.
- Internal vs. external trainers: Businesses can choose to hire external trainers or allocate internal resources to train employees on using the ERP system. Both options have cost implications and should be considered based on the company’s needs and resources.
- Time investment: Training employees on a new ERP system requires time and effort, which can impact productivity during the transition period. This indirect cost should be taken into account when estimating the overall implementation expenses.
Estimating ERP Implementation Costs
To make informed decisions about ERP implementation, businesses must accurately estimate the costs involved.
This process requires a clear understanding of the project’s scope, as well as thorough calculations for software, hardware, customization, and training expenses.
In this section, we will discuss the steps businesses should take to estimate ERP implementation costs effectively.
Identifying the scope of the project
A well-defined project scope is essential for accurately estimating ERP implementation costs and ensuring a successful outcome.
This process involves a thorough analysis of the business processes and requirements, followed by selecting the most suitable ERP solution. In this section, we will discuss these steps in detail.
Defining Business Processes and Requirements:
- Business process mapping: Start by documenting and mapping the organization’s key business processes to gain a clear understanding of how the various functions are interconnected and which areas can benefit from ERP implementation.
- Identifying pain points: Determine the existing challenges or inefficiencies within the organization that the ERP system should address. This may include manual or repetitive tasks, data silos, or a lack of real-time visibility into operations.
- Establishing functional requirements: Based on the business process analysis and pain points, develop a list of specific functional requirements that the ERP system must fulfill to meet the organization’s needs. This can include features like inventory management, financial reporting, or supply chain management.
Selecting the Right ERP Solution:
- Matching requirements with solutions: Evaluate different ERP solutions in the market and compare their features, modules, and capabilities with your established functional requirements. This will help in identifying the solutions that best fit your organization’s needs.
- ERP Vendor evaluation: Research and compare various ERP vendors based on factors like industry experience, customer reviews, and pricing models. This will help in narrowing down the list of potential ERP solutions and making an informed decision.
- Requesting demos and proposals: Reach out to the shortlisted ERP vendors to request product demos and proposals. This will provide a better understanding of the software’s capabilities, user interface, and potential customization options, enabling a more accurate estimation of implementation costs.
Calculating software, hardware, and infrastructure costs
Accurately estimating the costs associated with software, hardware, and infrastructure is crucial for budgeting and decision-making in ERP implementation projects.
In this section, we will discuss the steps businesses should take to effectively calculate these costs.
Comparing Different ERP Vendors and Their Pricing Models:
- Obtaining quotes: Request quotes from multiple ERP vendors, detailing the software licensing fees, support costs, services, and any additional charges. Ensure that the quotes include all the necessary modules and features required by your organization.
- Comparing pricing structures: Analyze the different pricing models offered by ERP vendors, such as perpetual or subscription-based licenses, and consider their long-term implications on the overall cost of ownership.
- Assessing hidden costs: Be aware of any hidden costs, such as fees for software updates, data migration, or scalability, which could impact the total cost of the ERP system.
Evaluating Hardware and Infrastructure Requirements:
- On-premise vs. cloud-based ERP: Determine whether your organization requires an on-premise or cloud-based ERP solution, taking into account factors like data security, control, and cost implications. Remember that on-premise solutions often involve higher upfront costs for hardware and infrastructure, while cloud-based solutions typically have lower initial costs but ongoing subscription fees.
- Hardware assessment: For on-premise ERP implementations, assess the necessary hardware, such as servers, storage, and networking equipment, required to support the ERP system. Calculate the costs associated with purchasing, installing, and maintaining this equipment.
- Infrastructure considerations: Evaluate the infrastructure requirements for the chosen ERP solution, including power and cooling resources, backup and disaster recovery solutions, and any additional facilities needed to house the hardware. Include these costs in your overall budget estimation.
Budgeting for customization, integration, training, and support
Estimating Costs for Customization and Integration
- Customization requirements: Based on your organization’s specific needs, determine the extent of customization required for the ERP system. This can include modifications to workflows, and user interfaces, or adding industry-specific functionalities.
- Integration needs: Identify the existing business systems that need to be integrated with the ERP solution, such as CRM, HR, or finance software. Consider the complexity of these integrations and their impact on the overall project cost.
- Consulting and development expenses: Calculate the costs associated with hiring external consultants or allocating internal resources to develop customizations and integrations. Include these costs in your overall budget estimation.
Allocating Funds for Employee Training and Ongoing Support
- Training methods and resources: Determine the most suitable training method for your organization, such as instructor-led sessions, online courses, or self-paced learning materials. Consider the costs associated with each method and allocate funds accordingly.
- Internal vs. external training: Decide whether to hire external trainers or use internal resources for employee training on the ERP system. Factor in the costs associated with each option and include them in your budget estimation.
- Support and maintenance: Assess the ongoing support and maintenance costs for the chosen ERP solution, including vendor support fees, costs of in-house support teams, and expenses related to software updates and upgrades. Allocate funds in your budget to cover these ongoing expenses, ensuring smooth operation and long-term success of the ERP system.
Tips for Reducing ERP Implementation Costs
Implementing an ERP system can be a significant investment, but there are ways to reduce costs while still achieving the desired outcomes.
In this section, we will share some practical tips for minimizing ERP implementation expenses without compromising on quality or functionality.
1. Carefully selecting the right ERP solution
Selecting the right ERP solution is crucial for successful implementation and maximizing ROI.
Begin by defining your organization’s specific needs, and consider industry-specific solutions to reduce customization costs.
Opt for a scalable, flexible system from a reputable vendor with a proven track record. Ensure seamless integration with existing business systems and choose a solution with an intuitive, user-friendly interface to minimize training costs.
Consider the total cost of ownership and the expected implementation timeline, and request product demos and trials to evaluate the software’s capabilities, ensuring the best fit for your organization.
2. Select an Experienced ERP Implementation Partner
Choosing an experienced ERP implementation partner can make a significant difference in the success of your project.
While their pricing might be higher, the investment ensures that the ERP system will be implemented effectively, reducing the risk of complications or failures. In contrast, opting for cheaper, less experienced partners may seem more cost-effective initially, but it can lead to potential setbacks, additional expenses, or even project failure.
By selecting a seasoned implementation partner, you gain the peace of mind that your ERP project is in capable hands and will deliver the desired results for your organization.
3. Leveraging existing hardware and infrastructure
One of the best ways to minimize ERP implementation costs is by taking full advantage of your organization’s current hardware and infrastructure.
Before jumping into purchasing new equipment or upgrading facilities, assess the compatibility and capacity of your existing resources.
For instance, evaluate your current servers, storage, and networking equipment to see if they can effectively support the chosen ERP solution.
In the case of cloud-based ERP systems, make sure your internet connectivity and network infrastructure are up to the task of handling the increased data traffic.
By leveraging the resources you already have in place, you can not only minimize upfront costs but also streamline the implementation process, reducing disruptions to your day-to-day operations.
4. Prioritizing customization and integration needs
When implementing an ERP system, it’s essential to strike a balance between meeting your organization’s unique needs and keeping costs under control.
To do this, prioritize the most critical customizations and integrations that will deliver the most significant impact on your operations.
Begin by identifying the key business processes and functionalities that the ERP system should address. Focus on customizations that will directly improve efficiency, reduce manual tasks, or enhance decision-making capabilities.
Similarly, prioritize integrations with existing systems that will streamline data flow and eliminate data silos.
By concentrating on high-impact customizations and integrations, you can optimize the return on investment while minimizing the overall implementation costs.
This approach also ensures that your organization reaps the maximum benefits from the new ERP system without getting bogged down by unnecessary modifications.
5. Implementing a phased approach to reduce risks and costs
A phased approach to ERP implementation offers several advantages, including reduced risks and costs.
By breaking down the process into manageable stages, you can focus on specific modules or functionalities, enabling better resource allocation, minimized disruptions, and improved employee adoption.
Introducing the new system gradually allows employees to adapt more effectively and ensures the organization can continue operating smoothly during the transition.
Additionally, spreading out the costs over an extended period makes budgeting and cash flow management more feasible, particularly for organizations with limited financial resources.
6. Investing in employee training and change management
The success of your ERP implementation hinges on investing in employee training and effective ERP change management.
Empower your workforce with targeted training using cost-effective methods, such as online courses or training key staff members who can teach others.
This fosters continuous learning and helps employees stay up-to-date with system updates.
Additionally, establish a robust change management strategy, clearly communicating the benefits and goals of the implementation, addressing concerns, and providing ongoing support.
By prioritizing employee training and change management, you create a foundation for long-term success and ensure a higher return on your ERP investment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing ERP implementation costs in Malaysia effectively requires businesses to carefully consider several key factors.
These include selecting the right ERP solution, partnering with an experienced implementation team, leveraging existing resources, prioritizing customization and integration needs, adopting a phased approach, and investing in employee training and change management.
By understanding and addressing these aspects, organizations can minimize costs while maximizing the benefits of their ERP system.
Businesses must be mindful of ERP implementation costs, as a well-planned investment can lead to improved efficiency, streamlined operations, and sustainable growth.
Embrace the transformative potential of ERP systems, and give your organization the competitive edge it needs to thrive in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
Additionally we recommend you to check you cost of Dynamics 365 which gives you more precise number how much it would cost to implement Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP or CRM applications.
Cost of ERP FAQs
In this section we will answer some of the most frequently asked questions about the cost of ERP system: