E-Invoicing: Malaysia to Enforce Starting from June 2024
Electronic invoicing (e-invoicing) is set to become a part of business operations in Malaysia. The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM, also known as LHDN) aims to create a platform where all e-invoicing must be submitted for validation. Initially, businesses with an annual turnover of over RM 100 million will need to adopt e-invoicing by June 2024.
E-Invoicing: Explained
According to the latest guidelines by IRBM, the body will be using Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) Model where the e-invoicing approval will be done instantly.
For the overall process, please refer to the infographic provided by IRBM below:
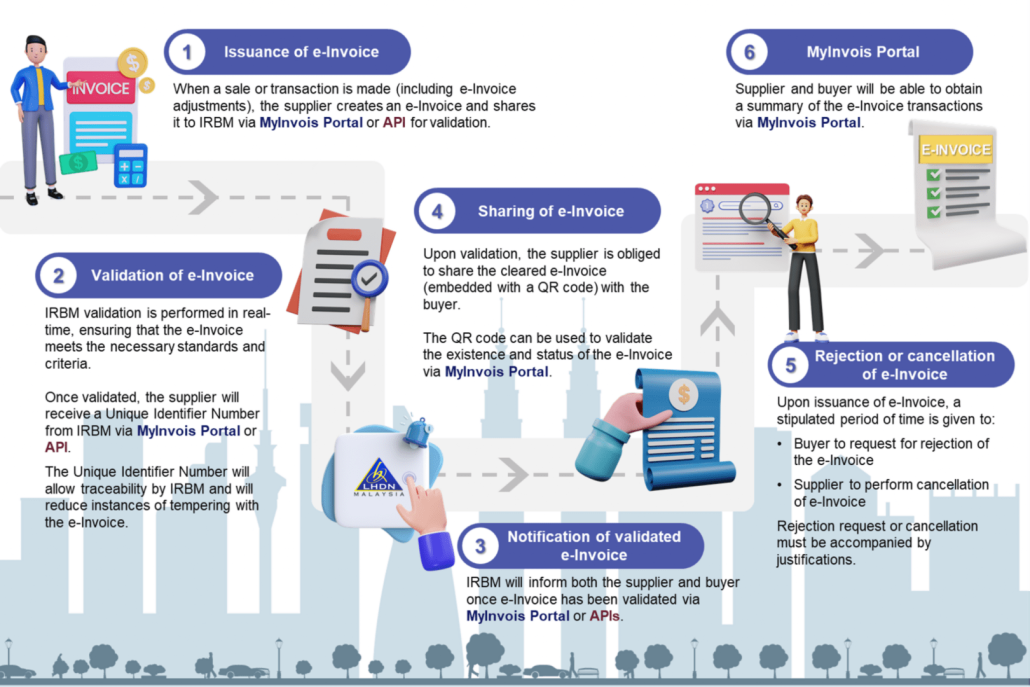
IRBM also has provided useful e-invoice guidelines & catalogues for businesses to use as a reference during the implementation process.
2 Methods of E-Invoicing
A. Application Programming Interface (API) Integration
- Use ERP software that is compatible with IRBM’s API.
- Saves time and effort, ensuring efficient submission of invoices.
- Suitable for big companies that involves large number of transactions.
B. MyInvois Portal
- For companies that did not have ERP software.
- Fill up 53 fields manually, which can result in human error.
- Suitable for companies that has low number of transactions.

Who Are Required to Do E-Invoicing?
All taxpayers are required to start implementing e-invoicing by phase, depending on their annual turnover. However, they are welcome to start the implementation of e-invoicing earlier. By January 2027, e-invoicing will become mandatory for all taxpayers regardless of sales threshold.
The implementation schedule is shown below:
| Phase | Start Date | Annual Turnover |
| 1 | 1st June 2024 | More than RM100 million |
| 2 | 1st January 2025 | More than RM50 million |
| 3 | 1st January 2026 | More than RM25 million |
| 4 | 1st January 2027 | All taxpayers and some non-business transactions |
Advantages of E-Invoicing

- Accurate tax reporting through smooth integration system.

- Avoid human error from manual data entry.

- Improve efficiency by reducing time and cost of operations.

- Eliminates tax evasion and fraud among taxpayers.
Best ERP Software for E-Invoicing
For companies that involves many transactions, using ERP software for e-invoicing is the best option.
We have listed out 6 best ERP software in Malaysia.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is TIN?
Tax Identification Number, also known as Nombor Pengenalan Cukai. It is a unique number assigned to individuals and entities registered as taxpayers with IRBM. The TIN number is used by the IRBM to identify taxpayers and track their tax records. It is also utilized by the IRBM to monitor taxpayer compliance and detect tax evasion.
What is Peppol?
Type of interoperable e-invoicing framework that is most widely used, with more than 20 countries already adopting it, including Singapore, Australia, Japan, and many countries in Europe.
Which scenarios that require e-invoicing to be issued?
1) Proof of income: E-invoicing will be issued by the taxpayer when a sale or other transaction is made to recognize income.
2) Proof of expenses: E-invoicing issued by a supplier should be in place as evidence to support taxpayers’ expenses, such as purchase of goods and services, payment of business expenses, return of goods and discounts given. For purchases of goods or services from a foreign supplier, the IRBM states that the Malaysian party (the purchaser) will need to issue a self e-invoice to document such expense incurred. This is because foreign suppliers do not issue e-invoices under the MyInvois Portal and require the Malaysian taxpayer to issue a self e-invoice instead.
What information will be stored in e-invoicing system?
1) General Information: Including invoice number, e-Invoicing type, e-Invoicing purpose, e-Invoicing date (current date).
2) Supplier & Customer Information: Including the supplier and customer’s TIN, name, address, email address, 5-digit MSIC code, MSIC description, website, contact person, and contact number, company registration number/individual MyKad number/passport, SST registration number, currency, exchange rate.
3) Item Information: Including the description, quantity, unit of measurement (UoM), unit price, discount rate, discount amount, tax type, tax code, tax rate, and tax amount, tariff code, subtotal, total excluding tax, total including tax for each item on the invoice.
4) Validation Information: Including the IRBM Unique Identifier Number, validation date and time, and validation status of the invoice.
5) Digital Certificates / Signature: Digital Certificates will be issued to taxpayers to enable them to attach digital signatures to e-Invoices. The digital signature will verify that the submitted e-Invoice data originates from a specific taxpayer.
6) Additional Information (Optional): May include payment mode, supplier bank account, payment terms, payment amount, payment date, payment reference number, bill reference number, and other relevant information.
Can the e-invoicing be amended?
Businesses are allowed to adjust their e-invoices within 72 hours of issuing the original invoice. This grace period can be used to rectify any errors in the invoice. Here is a more detailed explanation of the 72-hours e-Invoicing grace period:
1) Businesses can reject or request cancellation of an e-invoice within 72 hours of issuing the original invoice.
2) After this period, modifications to e-invoices are not allowed.
3) If any changes are required after 72 hours, businesses must issue a new invoice, debit note, credit note, or refund.
4) It is important to maintain clear records of these adjustments and follow the regulations to ensure compliance with IRBM’s guidelines.
Interested to learn more about e-invoicing?
Book a FREE consultation session today!
*Our representative will contact you within 24 hours after submitting the form, this excludes weekends and public holidays.








